CERN LHC Particle Accelerator Construction (Los 1)
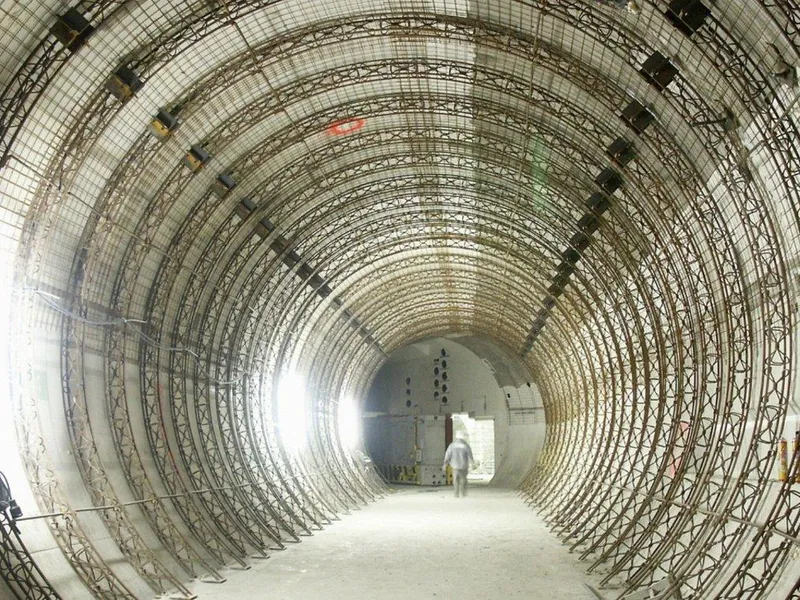
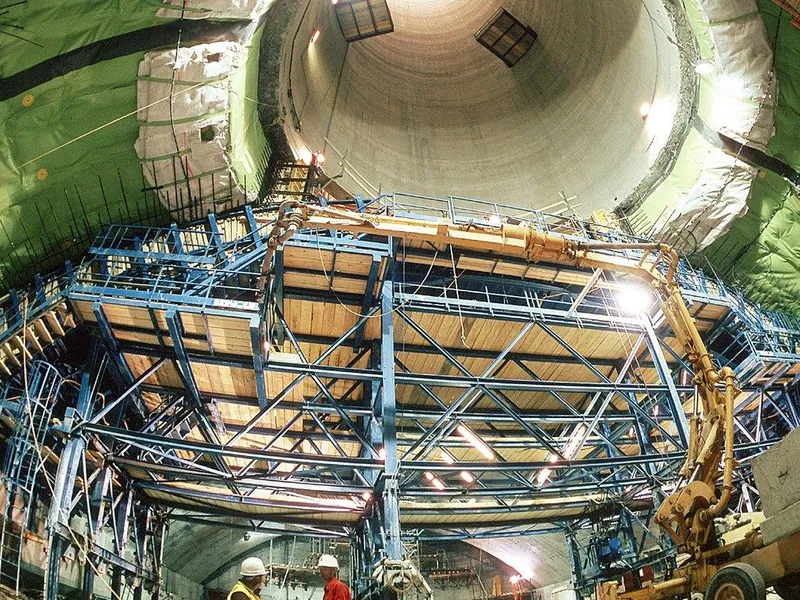
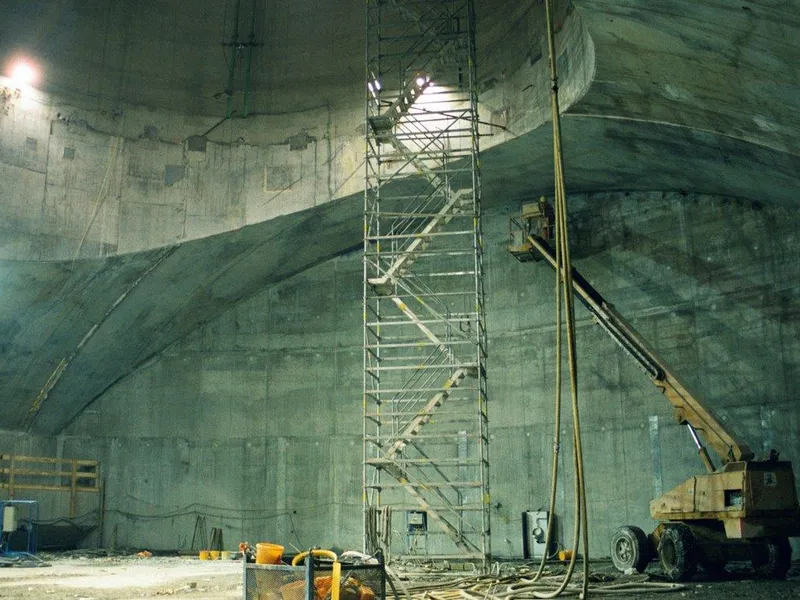
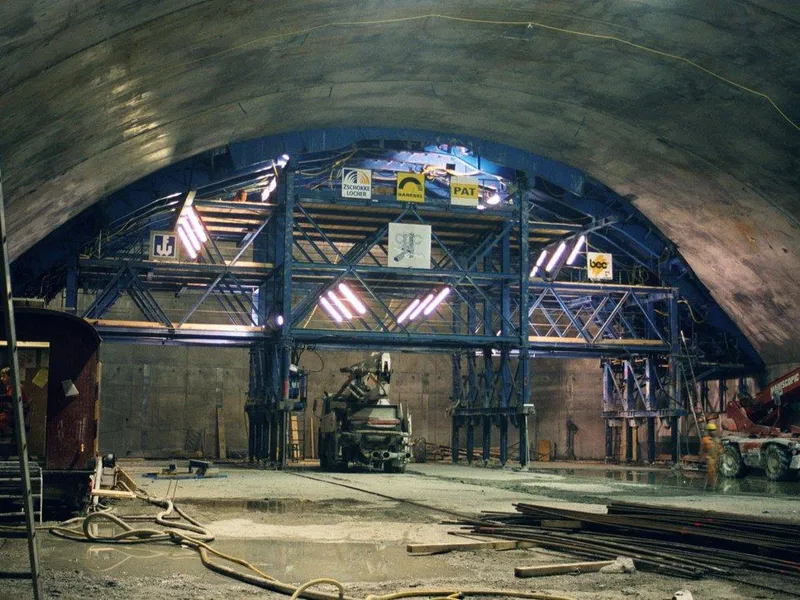
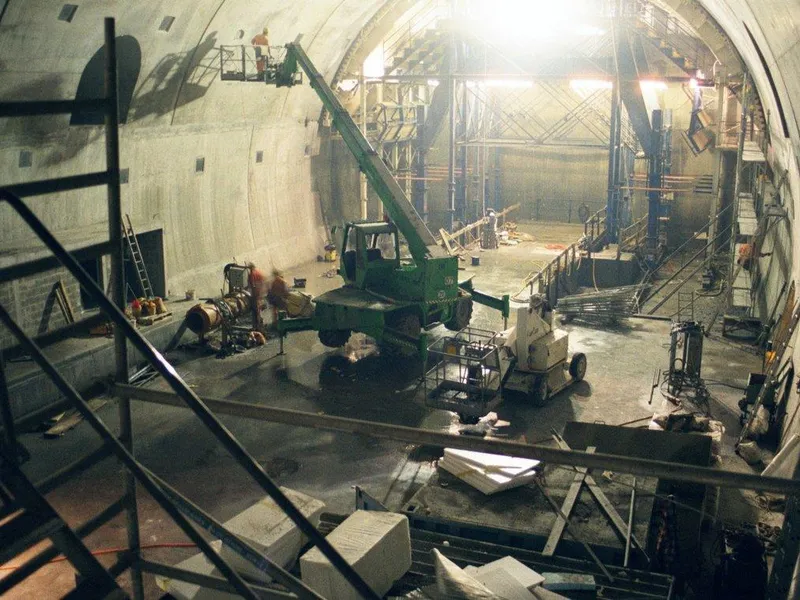
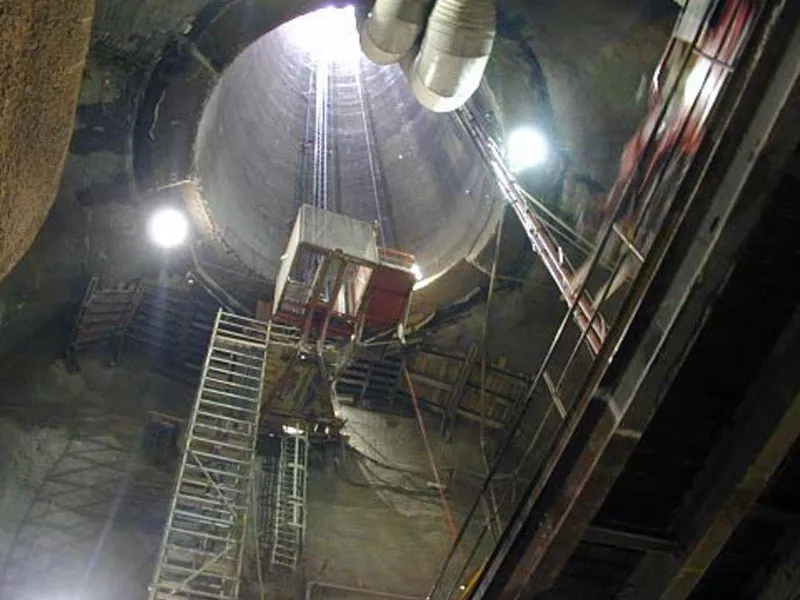
Beskrivelse: Implenia participated in building CERN's LHC particle accelerator, constructing multiple structures, including concrete buildings, shafts, and caverns, to aid groundbreaking research in physics. Les mer ↧
Fase: Ferdig bygd
| Byggestart | JANUARY 1998 |
| Ferdigstilles | DECEMBER 2002 |
Verdi og størrelse
106 mill

Miljøsertifiseringer
Ingen registrerte

Brannkonsept
Ingen registrerte
Aktører
 Arkitekt
Arkitekt
 Rådgivende ingeniør: 2 selskaper
Rådgivende ingeniør: 2 selskaper
Klikk på aktørene for å se kontakter
Juster hvilke aktører du ser her.

Dokumentsøk
concrete
shotcrete
tunnelbau
building
excavation
Kontakt oss på olav@pekeberg.com for å løfte dine nøkkelord til toppen
Selskaper og personer
Det er 8 selskaper koblet til dette prosjektet.
Lag en bruker eller logg inn for se navn, telefonnummer og e-post adresse til selskapene og kontaktpersonene (f.eks. prosjektleder hos entreprenørene).
Bilder
Kart
Klikk for å se tegnforklaringer
Oppdateringer
21. Mar 2025
- Byggestart lagt til: JANUARY 1998
- Prosjektverdi lagt til: 106 mill CHF
- CERN lagt til som Byggherre
- Implenia lagt til som Entreprenør
- Porr-Asdag Tunnelbau lagt til som Entreprenør
- C. Baresel AG lagt til som Entreprenør
- Wayss & Freytag AG lagt til som Entreprenør
- Bec-Perforex lagt til som Entreprenør
- Electricité de France lagt til som Rådgivende ingeniør
- Knight Piesold lagt til som Rådgivende ingeniør
Byggekamera
Har dette prosjektet et byggekamera?
Send oss en link på olav@pekeberg.com,
så legger vi det til her.